7.2 POSIX Process Management API
Process
- Closest to the informal idea of a running program
Process
- One or more threads
- Virtual memory accessible to those threads
- Other access rights
- Resource allocation context
- Other context (e.g. working directory)
Process Identification
- Each process has a process ID number (PID)
- All PIDs are positive integers

Process Creation
- Processes are created as a
forkof another - The only exception is the initial process created by the OS on boot
Fork
- The
forksystem call can be called from a thread to create a new process - The parent calling
forksees the process ID of the child as a return value - The child process sees a return value of 0
- The child process is otherwise an exact copy of the parent
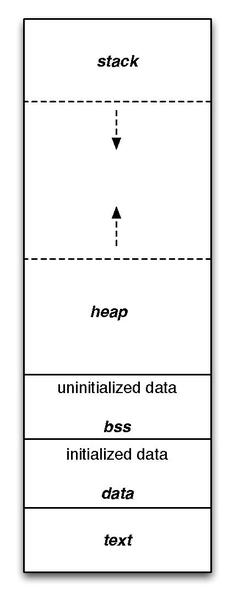
Memory
- A process created using fork holds copies of all memory available to the parent process
- This memory is a copy
- Memory is not shared as with threads
Multiprocessing
- Can be used to improve performance of parallel computations
- Provides different characteristics than threads
Running new programs
execcan be used to cause a process to begin running a new program
Fork and Exec
forkcreates a copied processexeccan be used to cause only the child to run a new program
Killing processes
killcan be used to send a signal to a specified process