Appendix A - Stacks
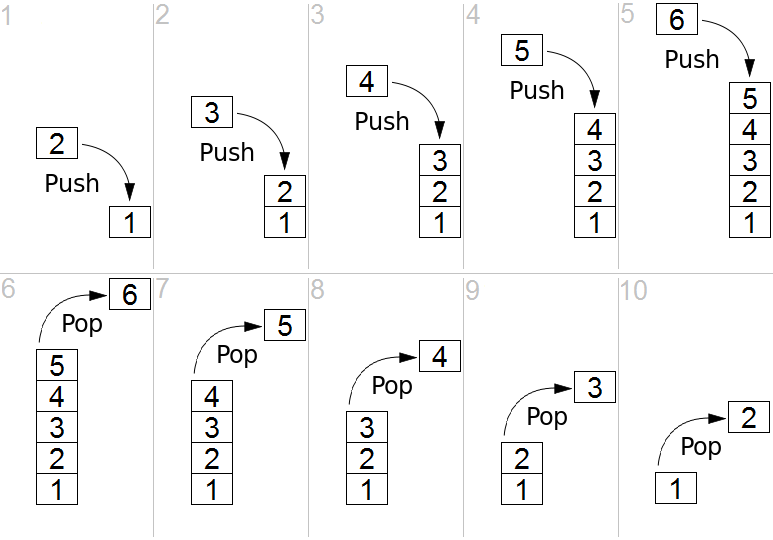
Stack Data Structure
- Abstract data type
- Supports
pushandpop - Last in, first out (LIFO)
Control Abstraction
- Create organized sections of executable code that execute in well-understood ways and can be reused
Subroutine
- Performs operations for the caller while the caller waits
- Arguments, or actual parameters, are passed to subroutines and mapped to formal parameters from the subroutine definition
- Subroutines that can return values can be called functions
Call Stack
- Memory space for functions to use to store local variables, return addresses, and other data
- Function calls push a new frame to the stack
- Returns pop their frame when they are finished with it
DrawSquare Example
Call stack review resources
Parameter Passing
Pass by Value
- Actual parameter values are made available to the subroutine
- Modification of values will not impact the caller
- This may involved making a copy in memory
Pass by Reference
- Actual parameters are references to data from the caller
- Modification of values will impact caller
- Should not involve copying data
C
- Pass by value
- If we want to be able to modify values, we need to pass values by reference
- We can’t do this is C, but we can use pointers passed by value to emulate it
If we allow C++, we can use a proper pass by reference mode.
Hardware
- Most ISAs pass values using a new stack frame and/or shared registers
- Hardware is necessarily pass by value
- Any pass by reference implementation needs to be built on values
Variable Numbers of Arguments
- It can sometimes be helpful to accept a different number of arguments
- One example of this is
printfin C
Function Returns
- End the function
- Return some value